Describe the Structure of the Urinary Bladder
Describe the structure and location of the urinary bladder. The bladder walls are mainly made up of muscle tissue but the inside of the bladder is lined with two different types of tissue.
The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves Teachmeanatomy
3 rows Key facts about the urinary bladder and urethra.
. Filtering Blood Removing Urine. Once food has been broken down and the body has. The urinary bladder functions as a storage vessel for urine to delay the frequency of urination.
Pages 21 Ratings 67 3 2 out of 3 people found this document helpful. School University of Phoenix. It has a folded internal lining known as rugae which allows it to accommodate up.
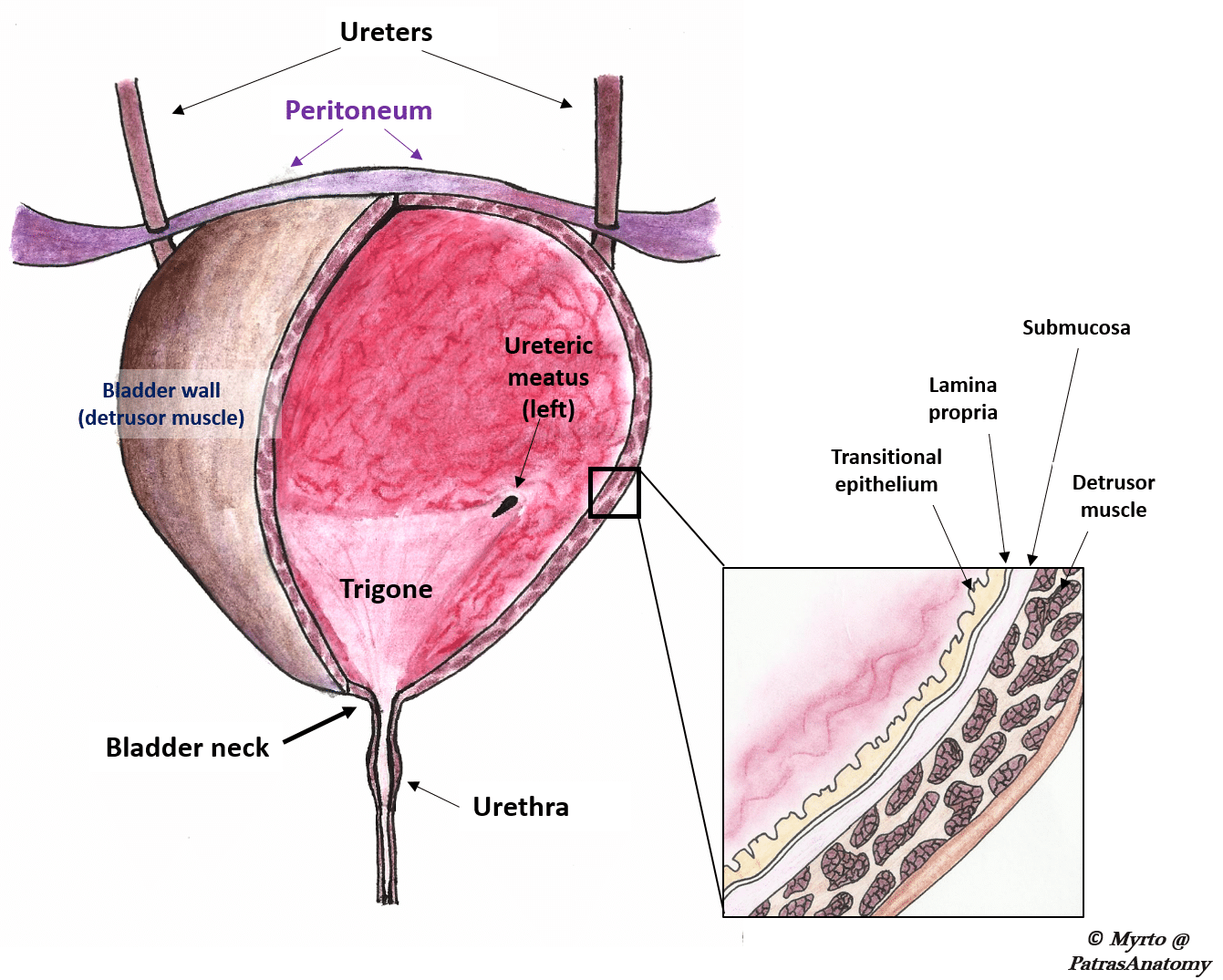
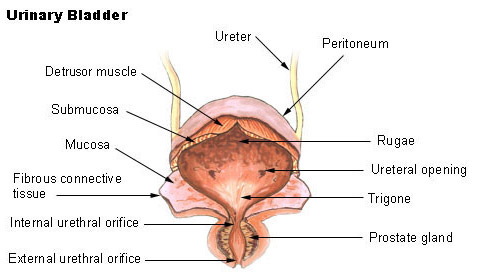
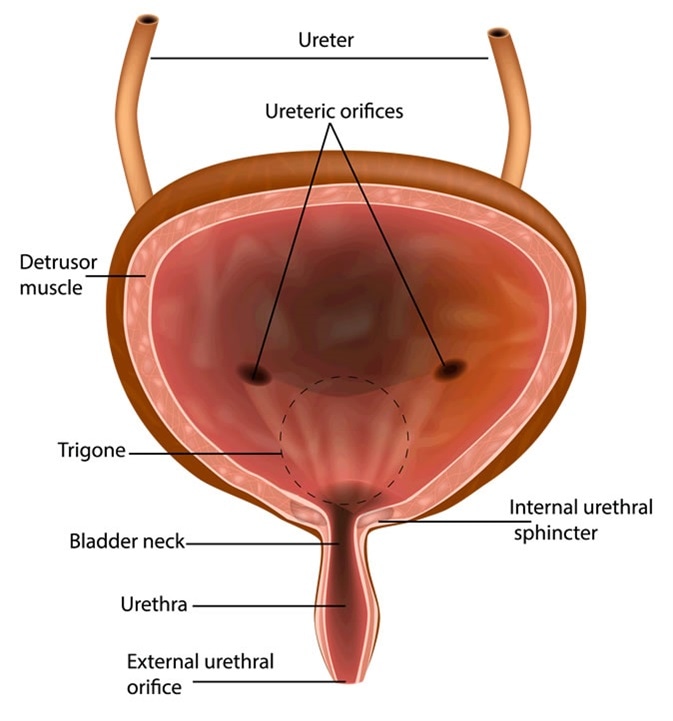
It receives urine via the ureters which are thick tubes running from each kidney down to the superior part of the bladder. Transitional epithelium elastic fibers and visceral muscle tissue in the walls of the. This triangle-shaped hollow organ is located in the lower abdomen.
In order to function properly the human body extracts nutrients from food and uses them to produce energy and repair damages. Each kidney connects to its own ureter which is a small tubular organ with a layer of muscle surrounding it that helps propel the urine into. Location - within the pelvic cavity posterior to the symphasis pubis and inferior to the parietal peritoneum.
The transitional epithelium layer is the first layer on the inside of the bladder. The structure and function of the urinary bladder. This acts as a lining that.
The structure and function of the urinary bladder urol int. Urine is collected in the body of the bladder and finally it is voided through the urethra. Describe the structure function of the urinary bladder The urinary bladder from BIOL 118 at University of Washington.
Features and Structure of the Bladder. Structure of the Bladder. The urethra is a tube which extends from the urinary bladder and opens outside the body and it allows the urine to pass outside the body.
The structure and function of the urinary bladder. Generally the bladder is a hollow muscular and pear-shaped distensible elastic organ that sits on the pelvic floor. How the Structures of the Urinary System Work 1.
The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys. Structure - distensible organ that is hollow and muscular. The urinary bladder is a balloon-like sac that receives the urine from the two ureters It stores the urine temporary until it is released outside the body through the urethra.
It is one of the most elastic organs of the body and is able to increase its volume greatly to accommodate between 600 to 800 ml of urine at maximum capacity. The bladders walls relax and expand to store urine and contract and flatten to empty urine through the urethra. Temporary storage of urine the bladder is a hollow organ with distensible walls.
Describe the structure of the urinary bladder hollow. Describe the structure of the urinary bladder Hollow distensible muscular organ. 1-3 The inside of the bladder is lined with a thin layer of cells which is called the urothelium.
These organs work together primarily to create store and eliminate waste namely urine. The bladder is partially retroperitoneal with its peritoneal-covered dome projecting into the abdomen when the bladder is distended with urine Figure 3. The bladder changes shape based on if it is empty or full of urine.
The first the internal urethral sphincter or IUS is composed of smooth involuntary muscle fibers internally and striated muscle fibers externally. Authors f bro-rasmussen a h sorensen e bredahl a kelstrup. When it is empty it looks like an inverted pyramid and when it is.
1Mucosanumerous folds 2Muscular layer has 3 distinctives layers of smooth muscle. The smooth muscle layer is a continuation of the detrusor muscle of the bladder. The Ureters Move Urine from the Kidneys to.
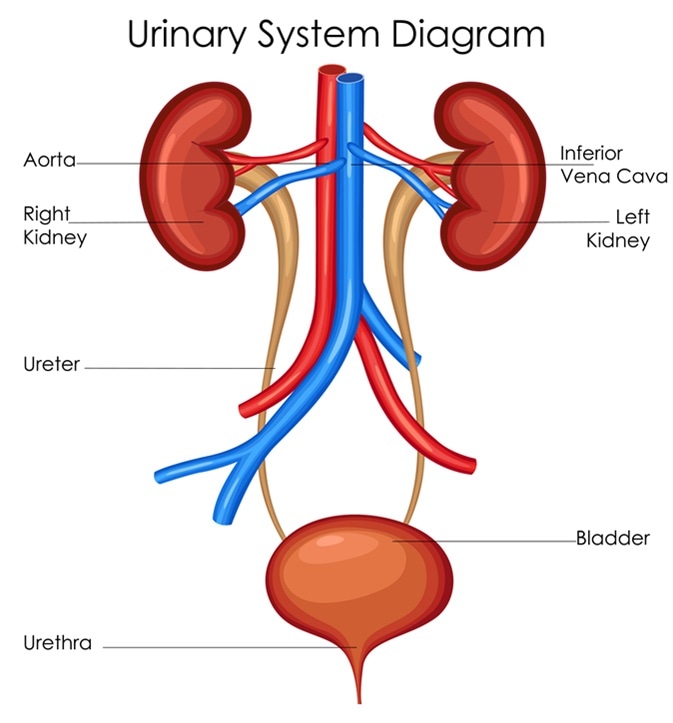
What are the basic layers that form the structure of the urinary bladder. Kidneys Filter Blood at the Top of the Urinary System The kidneys are bean-shaped organs situated on the back of the. The bladder divideS into two main parts each with its own features.
A hollow organ. It is located in the extraperitoneal space of the pelvis behind the pubic bones and extends into the abdomen when filled with urine. The urinary bladder collects urine from both ureters.
Course Title NSCI 281. Between this lining of cells the urothelium and the muscles of the bladder is another very thin layer of tissue called the lamina propria. It plays two main roles.
The bladder is an organ of the urinary system. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of. Vessels nerves lymphatics and ureters.
The upper part above the ureteric orifices is composed of the apex and body while the lower part is composed of the fundus trigone and neck. The bladder lies anterior to the uterus in females posterior to the pubic bone and anterior to the rectum. Structure of the Bladder when Expanding.
It is held in place by ligaments that are attached to other organs and the pelvic bones. The urinary system contains the kidneys bladder ureters and urethra. The urethra of both sexes has two sphincter muscles that close off the passage of urine.
The ureters are urine-bearing tubes that exit the kidney and empty into the urinary bladder.

Urine Transport And Other Structures Of The Urinary System Anatomy And Physiology
No comments for "Describe the Structure of the Urinary Bladder"
Post a Comment